Describe how triglycerides can be used in aerobic cell respiration and the nature. Describe the metabolic pathway of glycolysis how lactic acid is produced and the physiological significance of the lactic acid pathway.

Aerobic Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation 12 2 6 Cie A Level Biology Revision Notes 2019 Save My Exams
Fatty acids stored as triglycerides can be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids Breakdown of fatty acid releases.
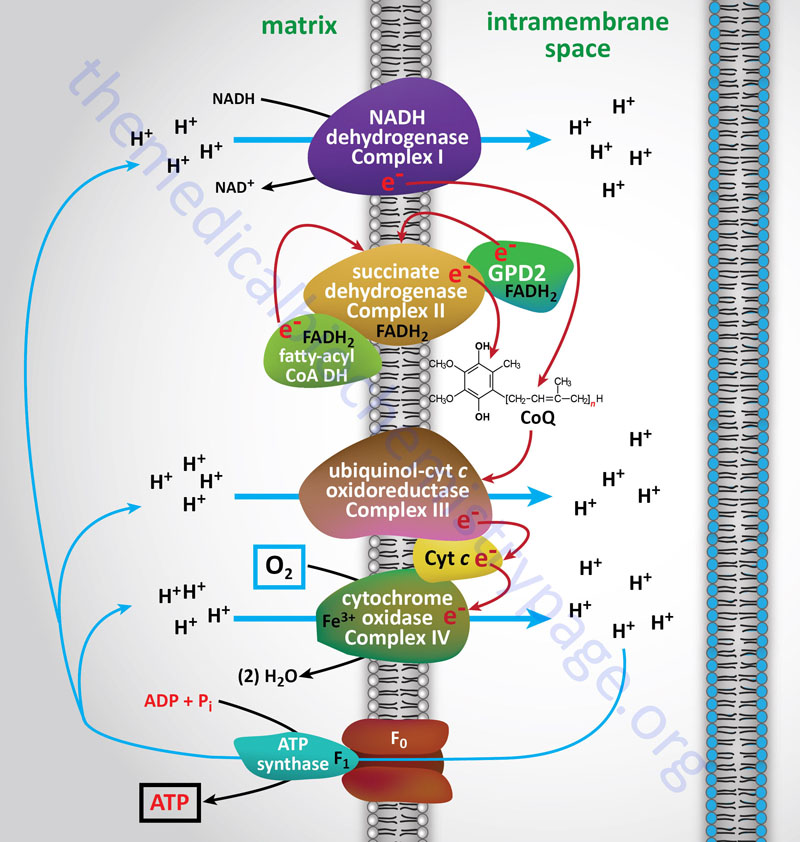
. NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the ETC. The energy from NADH and FADH 2 is used up. Triglycerides and phospholipids are broken down first by releasing fatty acid chains andor the phosphorylated head group in the case of phospholipids from the three-carbon glycerol backbone.
The most vital part of this process is the electron transport chain. Describe the relationships of glycolysis the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of their inputs and outputs. 30-36 ATP are recharged from ADP.
The electron is used in oxidative phosphorylation to synthesize ATP. Both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. The extra electrons on the oxygen attract hydrogen ions protons from the surrounding medium and water is formed.
It is also the method used in the light reactions of photosynthesis to harness the energy of sunlight in the process of photophosphorylationRecall that the production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation. 232 Describe the role of the nutrient pool in cellular metabolism. These include carbohydrates fat protein and alcohol Fig.
In oxidative phosphorylation the pH gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP. Triglycerides and phospholipids are broken down first by releasing fatty acid chains andor the phosphorylated head group in the case of phospholipids from the three-carbon glycerol backbone. Describe the electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation explaining the role of oxygen in this process.
For the generation of metabolic energy all major nutrients are degraded to acetyl coenzyme A acetyl-CoA. Such as cholesterol and triglycerides are also made from intermediates in these. Chapter 21 Glycolysis Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
Oxidative phosphorylation uses the chemical reactions that release energy to drive a chemical reaction that requires energy. Oxygen gas is converted into water. In oxidative phosphorylation the pH gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used.
Dehydrogenation and formation of ATP 2 triose bisphosphates are oxidized by removal of hydrogen to form 2 pyruvate molecules. In oxidative phosphorylation the pH gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP. These 2 sets of reactions are coupled and interrelated.
The released glycerol enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP whereas fatty acids are turned into acetyl-CoA in a process called beta-oxidation. The reactions breaking down triglycerides are catalyzed by lipases and those involving phospholipids are catalyzed by phospholipases. TCA cycle and beta-oxidation of fatty acids produce NADH and FAHD2.
Establishes a proton gradient used to make ATP Oxidative phosphorylation. During this process electrons are exchanged between molecules which creates a chemical gradient that allows for the production of ATP. The energy of the electrons is used to generate ATP.
The electrons that flow through electron transport chain is an exergonic process and the synthesis of ATP is an endergonic process. Chemiosmosis Figure 714 is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism. Many cells prefer glucose but can use triglycerides Adipose cells skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and liver cells use triglycerides as the primary energy source.
Describe the general structure of triglycerides and how glucose is transformed into triglycerides. Lysis molecule splits into 2 triose phosphates 3. Phosphorylation another Pi added to each triose phosphate forming 2 triose bisphosphate 4.
The entirety of this process is called oxidative phosphorylation. Couples the movement of substances across a membrane to chemical reactions. Thus oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
In stupid people terms describe the steps of oxidative phosphorylation. The reactions breaking down triglycerides are catalyzed by lipases and those involving phospholipids are catalyzed by phospholipases. Describe how electrons move through the electron transport chain and what happens to their energy.
When needed these triglycerides can be broken down in the cytoplasm into glycerol and fatty acids in a process called lipolysis. Oxidative phosphorylation is a highly efficient method of producing large amounts of ATP the basic unit of energy for metabolic processes. -electrons and H go from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria which are sites of. Describe how electrons move through the electron transport chain and explain what happens to their energy levels during this process. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process where energy is harnessed through a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner-membrane of mitochondria called the electron transport chain and ATP synthase to create ATP.
Their energy is used to pump protons H from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Describe lipolysis and how lipids can be used for energy including beta oxidation gluconeogenesis and. 74 Oxidative Phosphorylation Describe how electrons move through the electron transport chain and explain what happens to their energy levels during this process in the first complex two electrons are carried by NADH to it in the second complex FADH releases electrons to enzyme Q which also obtains the electrons from NADH.
Humans have a significant amount of energy stored as fat in the adipose tissue. Phosphorylation 2ATP provide 2 Pi to attach to a glucose forming hexose bisphosphate 2. This causes electron flow coupled with the transport of H.
Describe the essence of oxidative phosphorylation High energy electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are used to reduce O2 to H2O. 1 Oxidation of NADH and FADH and 2 Phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway through which cells release the energy stored in carbohydrates fats and proteins to produce adenosine triphosphate the main source of energy for intracellular reactionsThe process takes place within the mitochondria and involves oxidation-reduction reactions and the generation of an electrochemical gradient by the.
Lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides are also made from. Oxidative phosphorylation can be broken down into two parts. Acetyl-CoA is also called activated acetic acid because it consists of an acetyl acetic acid group that is bound to.

Oxidative Phosphorylation Superprof

1 Division Of Oxidative Phosphorylation Into Modules Arrows Marked E Download Scientific Diagram

Oxidative Phosphorylation And Related Mitochondrial Functions The Medical Biochemistry Page
0 Comments